if
- else & if - elseif - elseif - ….. else & nested if structures
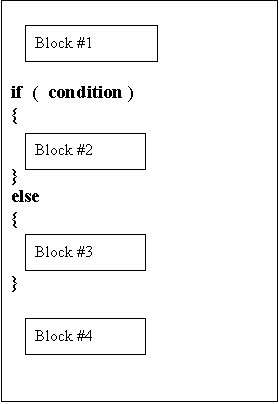
A more complex form of the selection structures is given by if - else .
Look at the following diagram:
|
|
Sequence of statement execution: Block #1 will be executed The condition of the if statement will be checked If the condition is true
then block#2 will be executed and then block#4 If the condition is false
then block#3 and then block#4 will be executed |
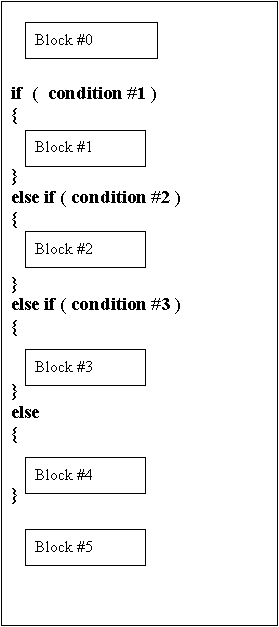
Even more complex structures can be obtained by the use of if - elseif - elseif - ….. else
See the following diagram
|
|
Sequence of statement execution: Block#0 will be executed Condition#1 of the if statement will be checked If condition#1 is true then block#1 will be executed and
then we will jump to block#5 If condition#1 is false then condition#2 will be checked If condition#2 is true
then block#2 will be executed and then we will jump again to block#5 If condition#2 is false
then condition#3 will be checked And so..on and so..on If all conditions are false
then block#4 will be executed and then block#5 |
An interactive example: enter a value for x in the box and watch the output of the following segmant of a program:
( the blue shade indicates the active section of the structure)
![]() x
=
x
=
|
The code segmant: |
The output: |
|
a = 0.0; b = 0.0; cout << “\n\n all variables are initialized to zero; if ( x <= 0.0 ) { a = 1.0; b = 1.1; cout << “ \n\n you entered a negative x “; } else if ( x > 0.0 && x <= 1.0 ) { a = 2.0; b = 2.2; cout << “ \n\n you are in the range (0.0,1.0]”; } else if ( x > 1.0 && x <= 10.0 ) { a = 3.0; b = 3.3; cout << “ \n\n one to ten is wide range “ ; } else { a = 100.0; b = 100.0; cout << “ \n\n unrealistic value for x “; } cout << “ \n\n a = “ << a << “ and b= “ << b;
|
|
Even
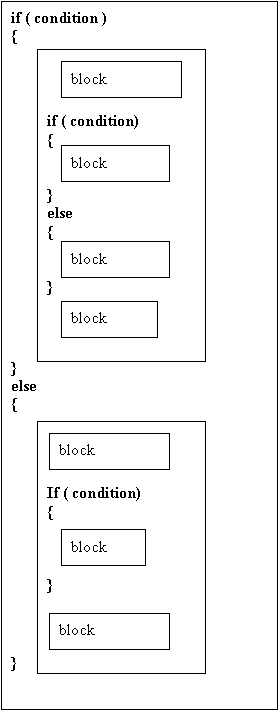
more complex if structures: Nested ifs
Since each block of instructions in an if structure can be any type of C++ code, it is possible to have other if structures as part of some of the blocks of the original if structure. The following diagram shows such a nested if structure:
![]()
© 2001 J.Y. Kazakia. All rights reserved.