MATLAB: Control Structures- loops
As you read this
material we strongly recommend that you activate your MATLAB window and try
the commands explained right there and then
In MATLAB we will use the while
and for loops. They are very similar to the ones we learned in C++. The
following tables illustrate the similarities/differences:
|
while structure in C++ |
while structure in
MATLAB |
Differences |
|
while( fabs(dx) > 0.0001) { fprime = 3*pow(x,2) - 5; f = pow(x,3) – 5 * x + 3; dx = f / fprime; x = x – dx; } |
while( abs(dx) > 0.0001) fprime = 3*x^2 - 5; f = x ^ 3 – 5 * x +3; dx = f / fprime; x = x – dx; end |
Use abs
for absolute value No need
for brackets end plays the role of the bracket no need
for pow function, use ^ for exponent. |
The following pictures
illustrate a complete program in MATLAB which utilizes the above segment. The
condition is slightly different to make sure the program does not fall into an
infinite loop.

The results are shown here:

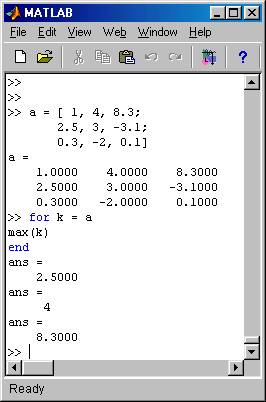
In the while structure, another difference between C++ and MATLAB is that the condition of
while may be actually a condition on arrays.
The following example illustrates this in a very simple way:

we see that as soon one of
the components of the array evaluates to false, the loop terminates.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
We can now study the for
structure. The following table illustrates the similarities/differences:
|
for structure in C++ |
for structure in MATLAB |
Differences |
|
for( k = 1; k <=10; k++) { factorial = factorial * k; cout << k <<” “<< factorial; } |
for k
= 1:1:10 factorial = factorial * k; fprintf(‘ %i %i’, k,factorial); end |
k=start:increment:end (if the
increment is not specified is taken as 1) No need
for brackets end plays the role of the bracket |
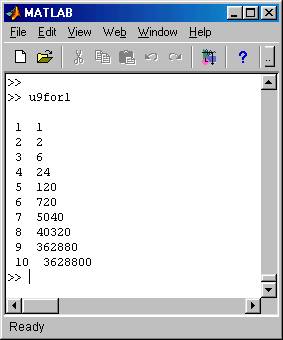
The following pictures show
the complete .m file and the results of running it in MATLAB.

Again in the for
structure, another difference between
C++ and MATLAB is that the for index may be actually set equal to a matrix. Then the loop starts by using as index the
first column of the array, then the second column etc. until the last column is
used.
The following example
illustrates this in a very simple way: