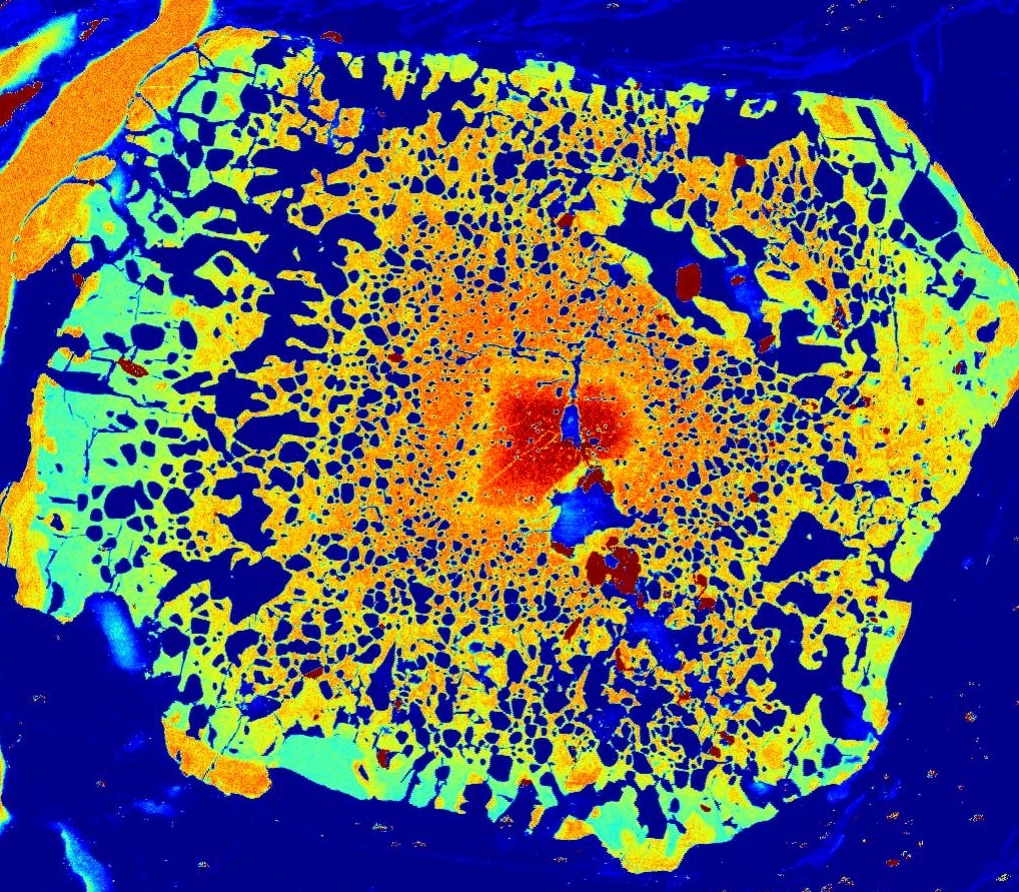
(see Bebout et al., 2022, a study of Li in these garnets)

Highlights:
Lead article, and cover in GSA Today, advertising the "Subduction Top to Bottom 2" publication project in the GSA journal GEOSPHERE (editors G. E. Bebout, D. W. Scholl, R. J. Stern, L. M. Wallace, and P. Agard; to see this Open Access article, click here)
GEOSPHERE
"Subduction Top to Bottom 2" Themed Issue
(completed; with 74 papers; click
here)
October 2013 issue of ELEMENTS on
"Nitrogen and its (biogeocosmo)chemical cycling"
(editors
G. E. Bebout, M. L. Fogel, and P. Cartigny; see the
cover of the issue here)
Recent review articles/book chapters
(invited):
Nitrogen
behavior during metasomatic alteration of UHP
whiteschists, Dora Maira,
work by Juan Felipe Bustos-Moreno, collaborative with Yi-Xiang Chen (USTC, Hefei, China)
and Hans-Peter Schertl (Ruhr University, Bochum), paper in
LITHOS, 2023
Carbon cycling in subduction zones: Record in HP/UHP metamorphic rocks, with work based in the Italian/French/Swiss Alps [collaborative with S. Angiboust, ENS. Lyon; P. Agard, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris; Marco Scambellluri and Laura Crispini, Università di Genova (see Cook-Kollars et al., 2014, and Collins et al., 2015, both papers in Chemical Geology; Scambelluri et al., 2016, Earth and Planetary Science Letters; Jaeckel et al., 2018, GEOSPHERE; recent research by Gabe Epstein, former Lehigh Ph.D. student; see Epstein et al., 2019, LITHOS, 2020, Chemical Geology)]
Volatiles cycling in
modern subduction zones — Example of the Hikurangi
margin, New Zealand: Ongoing,
NSF-funded research aims to elucidate the cycling of
volatiles (C, N, noble gases) across the Hikurangi
margin, North Island, NZ. This study involves
collaborations with researchers at the GNS Science (New
Zealand; Bruce Christenson), the University of Tokyo
(Hirochika Sumino), and the University of Minnesota
(Ikuko Wada). Subduction inputs at this margin are being
evaluated based in part on analyses of the C and N
concentrations and isotope compositions in the sediment
section entering the Hikurangi trench, using samples
recently recovered by IODP Expedition 375. Thermal
models of the margin have been merged with thermodynamic
calculations of devolatilization in the subducting
lithosphere/sediment section and outputs were evaluated
through analyses of volcanic and forearc cold seep gases
(see Epstein et al., 2021, G-cubed; click
here).

Nitrogen Isotope (GeoBio)chemistry:
Incorporation of N
during biotic/abiotic chemical alteration of seafloor
basalts and basaltic glasses (collaborative
with Eizo Nakamura, Katsura Kobayashi, Tsutomu Ota, and
Tak Kunihiro, IPM; Open Access article in Astrobiology;
click
here; additional articles in International
Journal of Astrobiology (Anderson et al., 2018), JGR-Planets
(Nikitczuk et al., 2022; click
here), and Astrobiology (Nikitczuk
et al., 2022; click
here)
Nitrogen cycling in
forearc mantle wedges, with analyses of
serpentinite seamounts at the Mariana margin (work by
Juan Felipe Bustos-Moreno, collaborating with Ivan
Savov, University of Leeds; paper in GEOLOGY,
2024)
Other recent or ongoing research:

We recently worked on C inputs into the
Sunda-Java margin (see House et al.,
2019, GEOLOGY). Locations for
DSDP/ODP Sites 211, 261, 262, and 765 are shown on the
seafloor topographic map above (image above is from
Smith and Sandwell Global Seafloor Topography, NOAA
and Scripps Institution of Oceanography).
Records of biogeochemical cycling of N (and other elements) in altered volcanic glasses (collaborative with Eizo Nakamura, Katsura Kobayashi, Tsutomu Ota, Tak Kunihiro, Christian Potiszil, and Ryoji Tanaka, IPM, Okayama University; recent work by Ph.D. student Matthew Nikitczuk; initial Open Access articles in Astrobiology; click here and Journal of Geophysical Research-Planets; click here; additional work underway by Juan Felipe Bustos-Moreno, also at the IPM)

Most of the research described here
is funded by the National Science Foundation — funding for the
research at the Institute for Planetary Materials is provided by
MEXT (Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and
Technology) and Okayama University, Japan.
_________________________________________________________________________